Core web vitals or CWB has been a hot topic in the SEO industry for the past few months.
What are Core Web Vitals ?
Core web vitals focuses on factors of the webpage that create good user experience like LCP (Least Contentful Paint), CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) and FID (first input delay).Optimizing these factors are helpful in enhancing user experience in terms of speed, visual stability and responsiveness of a web page. Hence Google is now taking them as one of the ranking factors.
Well that doesn’t mean if you optimize your webpage for CWV you will magically rank number 1 in search results. It is just one of the ranking factors among approx 200 ranking factors that google uses to rank a website. Google is not going to sacrifice the relevancy, trustworthiness of the webpage for just speed.

Why do you need to optimize for core web vitals ?
According to data available on the Search Console Help blog if the page increases from 1 second to 3 seconds then the bounce rate increases by 32% and if the page load time increases for 6 seconds the bounce rate increases by 106%. Increase in bounce rate will negatively affect your rankings.
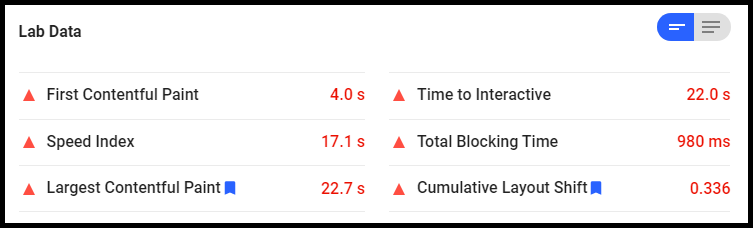
You can find core web vitals in the experience section of Google Search Console
What are LCP, FID and CLS ?
- What is LCP?
LCP stands for the largest contentful paint. The LCP measures the rendering time of the largest content (images, text, video etc.) within the viewport of the user. If the element extends outside the viewport then it does not count into LCP.
In other words, it measures the time taken from clicking a link to the loading of the largest content on the page visible to a real user. It is the most accurate way to measure the page speed because it is based on the time taken to render the largest element on the screen of the user once the page is loaded.
You can measure LCP score by using Google Pagespeed Insights or if you want more accurate data then look for this in Google Search Console under core web vitals section.
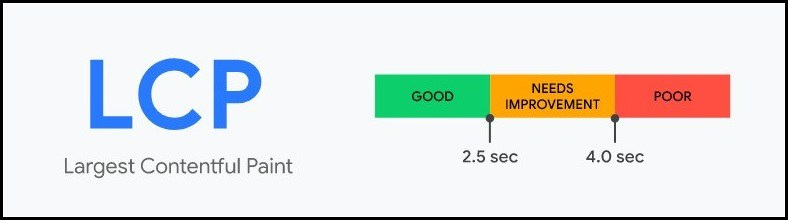
What is a good LCP score ?
Ideally, the LCP score should be less than 2.5 seconds.
How to improve your LCP score ?
- First find what type of above the fold content is taking time to load. It can be an image, fonts or videos.
- Minimize the size – compress images or if possible use webp format, use fonts recommended by google.
- Set up lazy loading
- Remove 3rd party scripts.
- Minify CSS: Mostly the header of a website has unused CSS or javascript that can be removed.
How to find unused JS and CSS ?
- Open google dev tools
- Press CTRL + Shift + P to open the command window.
- Type “coverage” in the search window and run the command. It will show window like this and red bars are unused JS and CSS
2. What is FID ?
FID or first input delay refers to the time taken by the browser to respond to the first interaction (click, touch or tab) of a user with your website. Faster the interaction, the more responsive the webpage is.
For Example – When a web page opens and you click on the “sign up” button. The time taken from click to execution of command (appearing of sign up pop up) is FID.
What is a good FID score ?
It is measured in milliseconds. A good FID score for a website is below 100 ms.

The cool part is that you cannot find this matrix in Google Page speed insights. The reason for this is simple – FID is measured by first input and it is done by a real user whereas page speed insights shows lab data.
Worry not!
For this you need to measure TBT (Total Blocking Time)
TBT refers to the total time for which your webpage is blocked thus preventing users from interacting with your web page. Larger the TBT, the more the FID score. The webpage is blocked because the main thread is executing javascript, html, CSS etc. So, minimizing main thread work is helpful in optimizing TBT and hence FID.

How to improve your LCP score ?
- Minimize or defer JavaScript.
- Remove or optimize CSS
- Remove 3rd party scripts
- Minimize main thread work – check in page speed insights.

3. What is CLS?
CLS stands for Cumulative Layout Shift. It is the unexpected shift of web elements that happens during the loading of a web page in your browser. The elements which can cause layout shifts are images, videos, fonts, buttons or ads.
The layout shift in a page causes poor user experience that’s why google has included it into the core web vitals. Some of this layout shift is easily visible through naked eye.
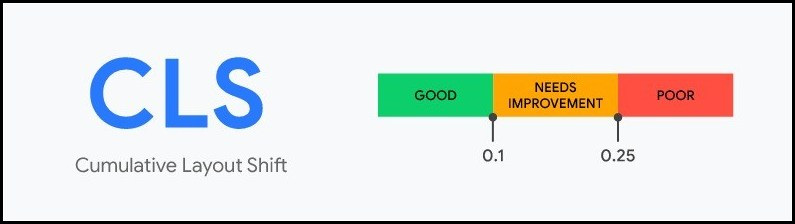
What is a good CLS score ?
For good user experience the CLS score should be less than 0.1.
What are the causes of Cumulative Layout Shift ?
- Image dimensions and size not defined.
- Ads, iframes dimensions are not defined.
- Improper use of web fonts.
In news websites or others which have ads, CLS is the most common problem.
How to check layout shifts on your webpage ?
To check layout shift follow these steps:-
- Open the website on your desktop and inspect it to open Google Dev Tools.
- Now go to performance and make sure core web vital is ticked
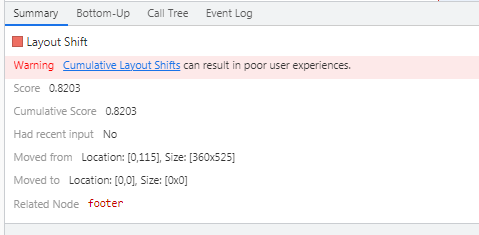
- Run this command and it will show a window like this
The dark red box shows the CLS in the webpage. Move the cursor onto it and it will show you the exact element which is causing CLS.
How to improve your CLS score ?
- To improve CLS score see the tips in Google Pagespeed Insights.
- Give height and width to all the webpage elements so that when the page loads the browser knows to keep particular space for ads, buttons etc.
If you are looking to optimize the speed of your website then Hire Me.
